A Mechatronic Design Engineer stands at the intersection of mechanical engineering, electronics, computer science, and control systems to create intelligent systems and advanced technologies. Mechatronics, a multidisciplinary branch of engineering, is an ever-evolving field that plays a vital role in modern industrial automation, robotics, manufacturing, and product development. The role of a Mechatronic Design Engineer is critical in ensuring seamless integration of hardware and software to build efficient, reliable, and smart systems.
What is Mechatronic Design?
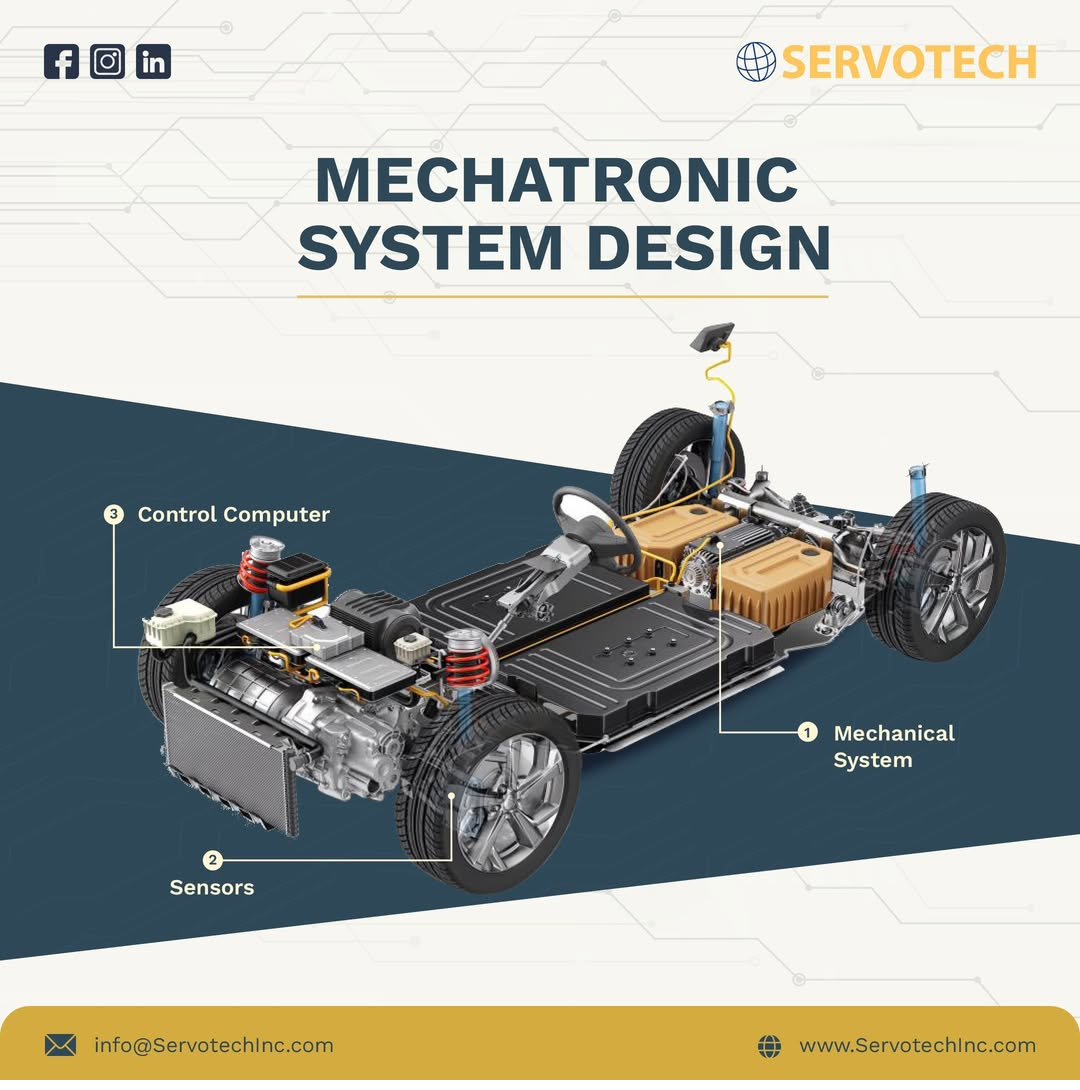
Mechatronic design is the process of designing systems that include mechanical components, electrical hardware, and embedded software. Unlike traditional mechanical systems, which operate independently of electronics, mechatronic systems are synergistic. A typical example of a mechatronic system is a robotic arm that integrates sensors, actuators, and microcontrollers to perform precise tasks.
The design process begins with understanding the system requirements, followed by concept generation, detailed design, simulation, prototyping, and testing. Mechatronic Design Engineers use software tools such as CAD for mechanical design, MATLAB/Simulink for control system simulation, and programming environments like C/C++ or Python for embedded coding.
Core Responsibilities of a Mechatronic Design Engineer
-
System Design and Integration
Mechatronic engineers are responsible for designing integrated systems that combine mechanical, electrical, and software components. They must ensure that all subsystems communicate efficiently and function harmoniously. -
CAD Modeling and Simulation
Mechanical components must be modeled using CAD software like SolidWorks or Autodesk Inventor. Engineers also simulate system dynamics and analyze performance using tools such as ANSYS or Simulink. -
Control Systems Development
Developing algorithms for motion control, feedback loops, and automation logic is crucial. These systems are often implemented on microcontrollers or programmable logic controllers (PLCs). -
Embedded Systems Programming
Writing firmware and embedded code for sensors, actuators, and controllers is a core part of the job. Languages such as C, C++, and Python are commonly used. -
Prototyping and Testing
Mechatronic engineers build physical prototypes to validate their designs. They conduct rigorous testing to ensure performance, reliability, and safety before product deployment. -
Collaboration Across Disciplines
Mechatronic engineers work closely with electrical, mechanical, and software teams. Strong communication and project management skills are essential for success in multidisciplinary environments.
Skills Required
To excel as a Mechatronic Design Engineer, a diverse skill set is required:
-
Strong Analytical Thinking: Understanding complex systems and solving multifaceted engineering problems.
-
Proficiency in Design Software: Mastery of CAD, CAE, and simulation tools.
-
Programming Skills: Embedded system development with languages such as C/C++, Python, and MATLAB.
-
Knowledge of Electronics: Understanding circuit design, PCB layout, and sensor technologies.
-
Control Theory and Automation: Applying feedback systems and automation strategies for optimal performance.
-
Project Management: Managing timelines, resources, and interdisciplinary collaboration.
Applications of Mechatronic Design
Mechatronic Design Engineers contribute to various industries:
-
Robotics
Robots for industrial automation, healthcare, and personal assistance are designed and developed using mechatronic principles. Engineers design the mechanical structure, embed sensors, and write control algorithms. -
Automotive Industry
Modern vehicles are embedded with numerous mechatronic systems such as anti-lock braking systems (ABS), adaptive cruise control, and electronic stability control. -
Aerospace
From avionics systems to drone technologies, mechatronics is integral to the development of lightweight, high-performance, and reliable aerospace solutions. -
Manufacturing Automation
Mechatronic engineers design smart machines and robotic arms that automate tasks like assembly, inspection, and packaging in manufacturing units. -
Medical Devices
Devices like prosthetic limbs, surgical robots, and diagnostic tools rely heavily on mechatronic design for precision and reliability.
Career Outlook and Opportunities
The demand for Mechatronic Design Engineers is growing rapidly due to the global push towards smart automation and intelligent systems. Industries are investing in advanced technologies to improve productivity, reduce costs, and enhance product capabilities. As a result, opportunities are available in sectors such as:
-
Robotics and Automation
-
Automotive and EV Development
-
Consumer Electronics
-
Aerospace and Defense
-
Biomedical Engineering
-
Industrial Equipment Manufacturing
Positions range from design engineer, automation specialist, robotics engineer, systems engineer, to R&D engineer. Many engineers also pursue advanced degrees or certifications in robotics, embedded systems, or artificial intelligence to stay competitive.
Education and Qualifications
To become a Mechatronic Design Engineer, a bachelor's degree in mechatronics, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, or a related field is typically required. Some universities offer dedicated mechatronics programs that blend mechanical, electronic, and computer engineering subjects.
Certifications and hands-on experience through internships, co-op programs, and personal projects can significantly boost a candidate’s profile. Familiarity with industry-standard tools, real-world design challenges, and team-based project experience are also important.
Future of Mechatronic Design
As the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and Industry 4.0 continue to shape the future, the role of Mechatronic Design Engineers will become even more prominent. The next generation of smart products will require even tighter integration of software and hardware, advanced sensors, real-time data processing, and autonomous decision-making capabilities.
Sustainability and energy efficiency are also influencing mechatronic design. Engineers are tasked with creating solutions that reduce energy consumption, enhance performance, and support a circular economy.
Conclusion
Mechatronic Design Engineers by Servotechinc are the architects behind the intelligent systems that power the modern world. They integrate multiple engineering disciplines to create efficient, adaptive, and smart solutions across various industries. With the rise of automation, robotics, and smart technology, the field of mechatronics offers exciting and dynamic career opportunities. It is a profession that not only demands technical expertise but also fosters creativity and innovation in solving real-world challenges.